This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.
 You can expect your healthy adult dog to poop 1-3 times daily, though this varies based on several factors.
You can expect your healthy adult dog to poop 1-3 times daily, though this varies based on several factors.
Puppies typically go more frequently (4-5 times daily), while senior dogs might go less often.
Your dog’s size matters too—smaller breeds usually poop more often than larger ones.
Diet quality directly impacts how often dogs poop; high-fiber foods increase frequency, while processed foods may slow things down.
Exercise also plays a role, as physical activity stimulates the digestive system.
While counting your pup’s bathroom breaks might seem strange, understanding their normal pattern helps you spot potential health issues early, and this understanding is crucial for maintaining your dog’s overall well-being.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Dog Poop Frequency
- How Often Dogs Poop
- Factors Affecting Poop
- Normal Dog Poop
- Poop Health Issues
- Maintaining Healthy Habits
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How often do puppies poop?
- How to determine if your dog’s poop is healthy?
- Can dogs poop more than 3 times a day?
- How long can a dog hold poop?
- How long can a dog go without pooping?
- How long after eating does a dog poop?
- How often should an adult dog poop?
- How long can a dog hold in poop?
- How long can dogs go without pooping?
- How long does it take for a dog to poop after eating?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Your healthy adult dog will typically poop 1-3 times daily, while puppies may go 4-5 times and senior dogs often decrease to once daily or less.
- Your dog’s poop frequency depends on several factors including diet quality (high-fiber foods increase frequency), exercise levels (physical activity stimulates digestion), and size (smaller breeds usually poop more often).
- You’ll know your dog’s poop is healthy when it’s chocolate-brown, firm but not hard, log-shaped, and free from concerning elements like blood, mucus, or undigested food chunks.
- You should maintain your dog’s digestive health through consistent feeding times, quality nutrition with proper fiber content, regular exercise, and veterinary check-ups to catch potential issues early.
Dog Poop Frequency
You’ll notice most healthy adult dogs typically poop between one to three times daily, depending on their diet, age, and activity level.
Your dog’s bathroom schedule can vary, with puppies needing to go more frequently (up to five times daily) while senior dogs often poop just once a day or even less, which can be considered a complete concept related to their diet.
Puppies may poop up to five times a day, while senior dogs often slow down to once daily or less—adapt their diet accordingly.
Normal Pooping Schedule
Most healthy adult dogs follow a regular poop schedule, typically going 1-2 times daily.
Your puppy, however, might need to go up to 5 times a day, usually 20-30 minutes after meals – making potty training a bit challenging.
Senior dogs often slow down to once daily or less, and establishing a routine is essential for understanding your dog’s normal bowel movements and holding time, regardless of breed differences.
Factors Affecting Defecation
Now that you know what’s normal, let’s look at what affects your dog’s poop schedule.
Your pup’s diet plays a major role – high-fiber foods increase dog poop frequency.
Hydration levels affect stool consistency, while medications can either speed up or slow down the process.
The gut microbiome, breed differences, and your dog’s emotional state all influence how often they need to go.
Even external factors like weather can impact your dog’s bathroom habits.
Age and Size Considerations
Your puppy’s tiny digestive system processes food like a high-speed train, resulting in up to five daily bathroom breaks.
As dogs mature, this frequency naturally decreases to one to three times daily. By their senior years, dogs often need fewer potty breaks.
Dog size impacts metabolism rates too – smaller breeds may need more frequent outings than larger dogs, despite producing smaller stools.
It’s also important to monitor their weight, as preventing obesity is essential in older dogs, helping to prevent obesity and ensuring a healthy life, with regular check-ups and a balanced diet.
How Often Dogs Poop
Now that you understand the basics of dog poop frequency, let’s look at the specific numbers. Your dog’s bowel movements follow patterns you’ll soon recognize.
Most adult dogs have predictable daily frequency patterns:
- Healthy adult dogs typically poop 1-3 times per day
- Puppies are poop machines, often going 4-5+ times daily
- Senior dogs usually decrease to once daily as their metabolism slows
- Small breeds tend to have more frequent bowel movements than larger dogs
- Active dogs generally poop more often than sedentary ones
Your dog’s individual variation is normal—some pooches are once-a-day performers while others have a more frequent dog poop schedule. What matters most is consistency in your dog’s normal pattern. When you notice changes in your dog’s digestion routine lasting more than a day, it’s worth paying attention to changes in digestion and considering the overall health of your dog.
Factors Affecting Poop
Your dog’s bathroom habits are influenced by several key factors including diet quality, feeding schedule, exercise levels, and environmental stressors.
Understanding these elements will help you establish what’s normal for your pet and recognize when changes might signal health concerns.
Diet Composition and Quality
What goes into your dog’s bowl directly impacts what comes out the other end.
High-quality dog food with proper fiber content and balanced protein sources substantially affects poop frequency and consistency.
Dogs eating nutrient-dense diets with appropriate grain inclusion typically have more predictable bathroom habits than those on low-quality food.
Premium ingredients support better dog digestion, while raw feeding can dramatically alter stool characteristics compared to processed options.
Adequate fiber is key, so consider supplementing dog’s diet if needed, to support better dog digestion.
Feeding Schedule and Portion Sizes
Beyond what you feed your dog, when and how much you feed them directly impacts their bathroom schedule. Your dog’s digestion typically triggers a bowel movement 8-12 hours after eating.
Meal timing matters—feeding twice daily usually results in two poops. Portion control prevents overloading the digestive system.
Understanding proper food measurements can aid in maintaining digestive health. Puppy feeding requires smaller, more frequent meals, while senior diets often mean less frequent elimination.
Finding the right dog meal frequency and poop patterns takes observation and consistency.
Daily Activity and Exercise Levels
Your dog’s activity level directly affects their bathroom schedule.
Regular exercise stimulates the digestive system, making potty breaks more predictable.
Active dogs typically have more frequent and consistent bowel movements than those with a sedentary lifestyle.
Walking your dog doesn’t just burn energy—it triggers natural mobility effects that promote healthy digestion.
A consistent dog exercise routine helps maintain regular elimination patterns, while changes in physical activity can temporarily alter their poop frequency, affecting their overall bathroom schedule and poop frequency.
Your dog’s activity level is crucial in determining their digestive health and bathroom habits.
Stress and Environmental Changes
Just as exercise affects your dog’s digestive system, stress and environmental changes can dramatically alter their bathroom habits.
Your furry friend’s bowel movements often reflect their emotional state.
When dogs experience anxiety or environmental shifts, their pooping patterns may change noticeably:
- Boarding facilities or travel often cause constipation or diarrhea
- Moving to a new home typically disrupts routine bowel movements
- Household changes (new pets/people) can trigger anxiety-related digestive issues
These changes can be significant, and understanding them is crucial for maintaining your dog’s health and well-being, especially during environmental shifts.
Normal Dog Poop
You’ll notice healthy dog poop is typically firm but not hard, with a chocolate-brown color and a consistent, log-like shape.
Firm, chocolate-brown, and log-shaped—your dog’s poop speaks volumes about their health.
Knowing what’s normal for your dog helps you spot potential health issues early, as changes in color, consistency, or contents can signal digestive problems or other medical concerns, which is crucial for identifying digestive problems.
Ideal Consistency and Color
A well-formed poop tells the tale of your dog’s internal health at a glance.
Your dog’s stool should be chocolate brown and firm enough to hold its shape while being slightly soft—think play dough consistency.
Sudden changes in color or consistency often signal dietary issues or health concerns that warrant attention.
| Consistency Factor | What It Indicates | Connection to Health | Ideal State | Warning Signs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydration Levels | Water balance | Kidney function | Moist but firm | Too dry or too wet |
| Fiber Content | Digestive efficiency | Gut Microbiome health | Holds shape | Crumbly or liquid |
| Bile Production | Digestive processes | Liver function | Brown color | Yellow or green tints |
| Fecal Consistency | Overall digestion | Intestinal health | Score of 3-4 on vet scale | Below 2 or above 5 |
| Dietary Supplements | Nutrient absorption | Balanced nutrition | No undigested food | Visible supplements |
The factors to consider when evaluating your dog’s stool include hydration levels, fiber content, bile production, fecal consistency, and dietary supplements.
Each of these factors provides insight into a specific aspect of your dog’s health, such as kidney function, gut microbiome health, liver function, and intestinal health.
Normal Size and Shape
Your dog’s poop should typically be shaped like logs or slightly segmented pieces, proportional to their size.
Smaller breeds produce marble-sized stools, while larger dogs create larger deposits.
The shape should be firm enough to maintain structure without being too hard.
Diet impact and hydration levels directly affect both size and form, with well-hydrated dogs producing more uniform stools.
Healthy dog stool should hold its shape when picked up.
Puppies, however, may experience variations, and unbalanced gut microbiomes are a common cause of soft stool.
Absence of Concerning Elements
While shape and size tell part of the story, healthy dog stool should be free from concerning elements.
Your dog’s poop shouldn’t contain mucus, blood, worms, foreign objects, or undigested food chunks.
Normal frequency combined with absence of these warning signs indicates proper dog digestive health.
Check for unusual colors like black, white-spotted, or gray stools, which might signal problems.
When in doubt about your dog’s bowel movements, consult your vet.
Poop Health Issues
You’ll need to check your dog’s waste regularly as changes in frequency, consistency, or color can signal serious health problems.
Watching for issues like blood in stool, persistent diarrhea, or straining without producing can help you catch potential blockages or infections before they become emergencies.
Intestinal Blockages and Symptoms
Intestinal blockages in dogs can quickly become life-threatening emergencies.
When your dog’s digestive tract gets obstructed by ingested objects, symptoms include vomiting, abdominal pain, lethargy, and changes in pooping patterns (either constipation or diarrhea).
Your veterinarian will need to perform a blockage diagnosis, possibly using imaging tests.
Surgical intervention is often necessary, followed by careful post-op care.
Implement preventative measures by monitoring what your dog chews and swallows.
Constipation can also arise from swallowing indigestible objects, which requires careful attention to your dog’s behavior and digestive health.
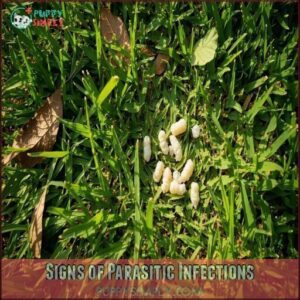
Signs of Parasitic Infections
A tell-tale sign of intestinal parasites in your dog’s poop is the presence of small, rice-like segments or spaghetti-shaped strands.
Watch for diarrhea, which often signals roundworms, hookworms, or tapeworms disrupting normal digestion.
Weight loss and scooting behavior are common red flags too.
If you notice your pup becoming lethargic or developing a dull coat, it’s time to collect a sample and schedule that veterinarian visit for proper diagnostic tests.
Blood in Stool and Potential Causes
While parasites may cause digestive issues, blood in your dog’s stool (hematochezia) requires immediate attention.
This alarming sign can indicate several health concerns:
- Bright red blood suggests lower intestinal or rectal bleeding
- Dark, tarry stools (melena) indicate upper GI bleeding
- Inflammation or dietary influences may also cause bloody stool
Don’t wait to contact your vet when you notice blood in dog poop—early intervention prevents complications and eases your mind.
Maintaining Healthy Habits
You’ll establish healthier poop habits for your dog by maintaining consistent feeding times, providing quality nutrition, and ensuring regular exercise throughout the week.
Regular veterinary check-ups will help you monitor your dog’s digestive health and address any potential issues before they become serious problems.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Everyone should schedule regular veterinary check-ups to monitor your dog’s digestive health.
Your vet can spot potential issues in your dog’s bowel movements before they become serious problems.
These visits allow for early detection of parasites or intestinal abnormalities through fecal testing.
Stick to vaccination schedules and discuss any changes in dog poop patterns during these appointments.
Consistent preventative care and health monitoring save you worry—and your pup discomfort—in the long run, which is a result of regular veterinary check-ups.
Balanced Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet directly impacts your dog’s bowel movements, making nutrition a cornerstone of digestive health.
To maintain healthy pooping habits, focus on:
- Proper fiber intake from vegetables and whole grains
- Adequate hydration (8oz per 10lbs of body weight daily)
- Quality protein sources without common allergens
- Probiotic-rich supplements to support gut flora
A healthy gut might need additional fiber sources to function properly, and watching for food allergies is crucial.
Watch for disruptions that could disrupt canine digestion and cause irregular bowel movements, as a healthy gut is essential for overall well-being.
Regular Exercise and Mental Stimulation
Regular walks do more than just prevent accidents in the house—they actually stimulate your dog’s digestive system. Taking your pup out for consistent daily exercise helps regulate bowel movements and maintains digestive health.
Different breeds have varying exercise needs that affect their digestion patterns. Mental stimulation through play and training can also reduce stress-related digestive issues.
Some pet owners use supplements, but it’s important to bear in mind supplement safety risks before adding them to your dog’s diet. Watch for behavioral changes during walks—they often signal how your dog’s bathroom routine is functioning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How often do puppies poop?
Like tiny poop factories, puppies typically defecate 4-5+ times daily.
You’ll notice they often go after meals.
This frequency gradually decreases as they age, eventually settling into the adult pattern of 1-3 times daily.
How to determine if your dog’s poop is healthy?
Healthy dog poop should be chocolate-brown, firm but not hard, and shaped like logs.
Check for consistency, color, and contents – watch for blood, mucus, worms, or foreign objects that indicate health problems.
Can dogs poop more than 3 times a day?
Yes, your dog can poop more than 3 times daily. It’s normal for puppies, active dogs, and those on high-fiber diets. Monitor consistency and behavior to determine if it’s healthy.
How long can a dog hold poop?
Most dogs can hold their poop for 8-12 hours, though this varies by age and size.
Puppies need more frequent breaks, while adult dogs shouldn’t be forced to hold it beyond their comfort.
How long can a dog go without pooping?
Worried about your furry friend’s bathroom schedule?
Most dogs can safely go 24-48 hours without pooping, but you shouldn’t let them hold it longer than that.
Watch for discomfort or unusual behavior.
How long after eating does a dog poop?
Your dog will typically poop 8-12 hours after eating, though puppies may go sooner. Most adult dogs defecate 30 minutes after meals or upon waking, making walks during these times effective.
How often should an adult dog poop?
Your adult dog should typically poop 1-3 times daily.
Patterns vary based on diet, size, and activity level.
Watch for consistency in their routine—it’s your best indicator of their digestive health.
How long can a dog hold in poop?
Healthy adult canines can typically hold their poop for 8-12 hours, though it’s not recommended.
You’ll notice your pet’s individual limits based on age, size, and health status.
Don’t make them wait unnecessarily, as this can help you understand their individual needs and ensure their health and well-being.
How long can dogs go without pooping?
Isn’t it ironic that while you’re waiting nervously, your dog’s actually quite comfortable?
Most healthy dogs can go 24-48 hours without pooping, but you shouldn’t wait longer than 48-72 hours before contacting your vet.
How long does it take for a dog to poop after eating?
Most dogs will typically poop within 30 minutes after eating as food triggers their digestive system. You’ll notice puppies respond even faster than adult dogs due to their quicker metabolism.
Conclusion
Monitoring how often do dogs poop is absolutely more valuable than a mountain of gold for responsible pet owners.
By tracking your dog’s bathroom habits, you’ll quickly notice when something’s off.
Remember, healthy adult dogs typically go 1-3 times daily, but this varies with age, size, diet, and exercise levels.
Trust your instincts—if your dog’s pooping pattern changes substantially, consult your vet.
Staying attentive to these details guarantees your furry friend remains happy and healthy.