This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.

Understanding the root cause separates effective treatment from endless frustration, turning a cycle of irritation into lasting relief. Recognizing warning signs early and addressing both medical and behavioral triggers protects your dog’s skin, health, and quality of life.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- Why Do Dogs Bite Their Legs?
- Identifying Signs of Leg Biting in Dogs
- Common Medical and Behavioral Triggers
- How to Stop Dogs From Biting Their Legs
- When to Seek Veterinary Help for Leg Biting
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- How do I stop my dog from biting his legs?
- Is it normal for dogs to bite legs when playing?
- How do you treat a dog chewing hair off hind legs?
- What does it mean when dogs bite their legs?
- How to stop a dog from biting legs?
- Are dogs playing when they bite legs?
- How do you know if a dog bite is serious?
- Can certain dog breeds be prone to leg biting?
- Does weather impact dogs biting their legs?
- How does age affect leg-biting behavior?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Leg biting in dogs stems from identifiable causes—allergies, parasites, infections, pain, or anxiety—and requires addressing the root trigger rather than just treating surface symptoms.
- Early recognition of warning signs like excessive licking, hot spots, hair loss, and behavioral changes prevents minor irritation from escalating into serious infections or chronic wounds.
- Effective treatment combines veterinary diagnosis with targeted interventions including parasite control, dietary adjustments, proper skin care, and behavioral modification tailored to the underlying cause.
- Certain symptoms demand immediate veterinary attention—severe bleeding, sudden lameness, exposed tissue, or systemic signs like fever—while chronic cases require long-term management strategies and routine monitoring.
Why Do Dogs Bite Their Legs?
When your dog won’t stop gnawing at their legs, it’s not just a quirky habit—it’s their way of telling you something’s wrong. The root cause could be physical discomfort, emotional stress, or even hardwired instinct.
Let’s break down the main reasons behind this behavior so you can figure out what’s driving your dog’s leg biting.
Dry Skin, Allergies, and Parasites
Among the most common triggers for leg biting, dry skin, allergies, and parasites top the list. Your dog’s itchy legs might stem from environmental factors, food sensitivities, or unwanted guests hitching a ride on their skin.
- Dry skin causes persistent itchiness, especially during winter months when indoor heating strips moisture from your dog’s coat and skin.
- Allergy symptoms from pollen, dust mites, or certain proteins trigger relentless scratching and chewing, creating redness and hot spots.
- Flea prevention and tick-borne diseases demand attention since fleas, ticks, and mite infestations cause intense irritation that drives compulsive biting behavior. Regular grooming can also help to reduce skin irritation.
Infections and Medical Conditions
Beyond surface-level irritants, bacterial pyoderma and fungal infections drive relentless leg biting in many dogs. Bacterial skin infections accounted for 8.70% of dermatological cases, while fungal conditions—including yeast overgrowth—represented 19.25% during recent surveys.
Hot spots develop rapidly when moisture and broken skin create breeding grounds for bacteria, and acral dermatitis from compulsive licking leads to scarring and chronic wounds.
Systemic conditions like hypothyroidism or diabetes also trigger secondary skin infections, making your dog’s legs a target for persistent chewing. Regular grooming can help prevent canine skin irritation.
Anxiety, Boredom, and Behavioral Causes
Sometimes, the problem isn’t physical—it’s in your dog’s head. A 2021 study found 72.5% of surveyed dogs displayed anxiety-related behaviors, and 80% of owners noted destructive behaviors when their dogs lacked mental stimulation.
Separation anxiety, social isolation, and environmental changes all fuel compulsive licking and leg biting. Dogs left alone for extended periods face double the risk of developing these canine anxiety patterns, turning boredom into a painful loop of self-injury.
Breed-Specific Instincts and Play Behavior
Not all leg biting comes from distress—your dog’s breed and natural play drive can trigger biting behaviors that look alarming but stem from hardwired instincts.
Herding breeds like Border Collies may nip at their legs during high-energy play, mimicking their herding instincts. Terrier digging motions can morph into leg chewing during excitement, while retriever instincts sometimes redirect mouthing behavior inward.
Scent hounds may bite when overstimulated by environmental triggers, transforming normal play styles into concerning canine behavior patterns.
Identifying Signs of Leg Biting in Dogs
Spotting leg biting early can prevent your dog from developing serious skin problems or infections. You’ll need to watch for physical changes on your dog’s legs as well as shifts in behavior that signal something’s wrong.
Here are the key warning signs that indicate your dog’s leg biting has become a problem.
Excessive Licking, Chewing, or Scratching
When your dog starts focusing on one spot—licking, chewing, or scratching the same area over and over—it’s usually a clear signal that something’s bothering them. These obsessive behaviors can quickly lead to paw granulomas or secondary infections if left unchecked.
Dog chewing behavior like this often stems from dog health problems, dog skin conditions, or dog behavioral issues that require attention. Behavioral modification and pain relief strategies depend on identifying whether canine behavior reflects discomfort or anxiety.
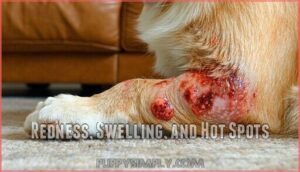
Redness, Swelling, and Hot Spots
If you spot angry red patches, puffiness, or those telltale hot spots on your dog’s legs, you’re looking at visible signs that irritation has already taken hold. These infection indicators point to underlying inflammation, often triggered by an allergy or relentless itch.
Hot spot treatment becomes urgent once the dog chews deep enough to compromise skin integrity—bite severity matters because secondary bacterial infections can quickly escalate.
Swelling causes range from bug bites to more serious dog skin conditions requiring veterinary attention.
Hair Loss and Skin Changes
Bald patches and altered skin texture signal that your dog’s chewing habit has crossed from surface irritation into chronic damage. Alopecia patterns reveal where the dog targets most often, while skin discoloration—from pink to brown—indicates inflammation duration.
You’ll notice:
- Texture changes ranging from thickened, leathery skin to raw, weeping areas
- Dandruff scales suggesting underlying allergies or fungal involvement
- Lesion types including crusts, erosions, or ulcers that demand immediate veterinary evaluation
These visible markers help you assess itchiness severity and guide dog health interventions.
Behavioral Changes and Discomfort
Beyond the visible wounds, your dog’s entire demeanor may shift—restlessness replaces calm, sleep patterns fragment, and once-loved activities lose their appeal. Vocalization changes—whining, whimpering—often accompany persistent licking.
You may observe sudden aggression when approached, appetite loss despite normal feeding routines, or social withdrawal from family interactions.
These behavioral issues reflect stress and anxiety, sometimes stemming from boredom or attempts to gain attention, signaling that discomfort has escalated beyond physical irritation.
Common Medical and Behavioral Triggers
Once you’ve spotted the warning signs, the next step is figuring out what’s driving your dog’s leg-biting habit. The triggers behind this behavior can range from physical discomfort to emotional stress, and identifying the root cause is essential for choosing the right solution.
Let’s break down the most common medical and behavioral factors that might be pushing your dog to bite their legs.
Allergies and Skin Infections
Allergies rank among the most common reasons for leg biting, affecting roughly 20–30% of dogs worldwide. Environmental triggers, food sensitivities, and fleas can all spark intense itching that drives your dog to chew and scratch relentlessly. Certain breeds—like West Highland White Terriers, Boxers, and English Bulldogs—face higher risk factors due to genetic predisposition.
Watch for clinical signs like redness, hair loss, and hot spots, which often signal secondary infections from yeast or bacteria. Treatment costs average $266 initially, climbing to $841 annually, reflecting the economic impact of chronic management trends.
Pain, Injury, and Joint Issues
When your dog fixates on biting a specific leg, you might be watching pain—not just an itch—drive that behavior. Arthritis signs, muscle injuries, or nerve damage can trigger localized discomfort that prompts repetitive chewing. Joint pain worsens with age, creating inflammation your dog tries to "fix" through licking.
Mobility issues often accompany musculoskeletal pain, signaling underlying medical conditions or disease that demand veterinary assessment before permanent damage occurs.
Stress, Anxiety, and Environmental Factors
Your dog’s mind plays as big a role as physical irritation. Stress and anxiety trigger compulsive chewing when dogs lack outlets for nervous energy or face environmental stressors like sudden routine changes.
Behavioral triggers include:
- Separation anxiety causing self-directed behaviors
- Boredom from insufficient mental stimulation
- Exposure to chemicals in household cleaning products
- Environmental allergies worsening anxiety-induced biting
Stress management requires addressing both emotional needs and environmental products that aggravate skin sensitivity.
Hormonal Imbalances and Underlying Diseases
Thyroid dysfunction, Cushing’s disease, and other systemic illnesses create internal imbalances that manifest as skin irritation and compulsive leg biting. Hypothyroidism slows metabolism, causing dry skin your dog wants to scratch constantly. Cushing’s disease weakens skin integrity, making it vulnerable to infections.
Diabetes Mellitus and autoimmune disorders disrupt immune function, while certain cancer symptoms include persistent itching. These underlying diseases require veterinary diagnosis because skin changes signal deeper health problems beyond surface irritation.
How to Stop Dogs From Biting Their Legs
Stopping your dog from biting their legs requires identifying the root cause and taking targeted action. Your vet can diagnose medical issues like infections or allergies, while you address behavioral triggers through routine changes and enrichment.
Here’s a breakdown of effective strategies to help your dog find relief and break the cycle.
Veterinary Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Your veterinarian will conduct a thorough physical examination, including blood work, urinalysis, and skin scraping to pinpoint medical causes like allergies or disease. Diagnostic imaging may reveal joint pain driving the behavior.
Treatment options include:
- Oclacitinib therapy for allergic dermatitis, reducing inflammation within weeks
- ASIT therapy (immunotherapy) for long-term allergy management
- Behavioral modification programs with anti-anxiety medications for compulsive biting
- Follow-up protocols to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed
Addressing both medical causes and behavioral causes ensures effective, lasting relief.
Parasite Control and Skin Care
Fleas, ticks, and mites don’t just irritate your dog—they’re often the hidden culprits behind relentless leg biting, and effective parasite control is your first line of defense. Monthly flea and worm treatments prevent infestations that trigger allergies and itch relief needs.
Regular tick control protects coat health while reducing skin inflammation.
Proper bathing frequency—every 4-6 weeks with moisturizing shampoos—maintains skin hydration without stripping natural oils, supporting your dog’s overall comfort.
Dietary Changes and Supplements
If you’ve ruled out parasites but your dog still can’t leave his legs alone, what goes into his food bowl might be fueling the fire. Food allergies and intolerances often trigger chronic itching, so switching to limited-ingredient diets helps identify problem proteins.
Improving gut health with probiotics bolsters immune function, while omega fatty acids—especially fish oil—reduce inflammation and promote healthier skin.
These diet changes, combined with essential fatty acid supplements, get to the source rather than just masking symptoms.
Mental Stimulation, Exercise, and Training Techniques
Sometimes a bored, under-exercised dog creates his own entertainment—and unfortunately, that means gnawing at his legs until you intervene. Puzzle toys and interactive games redirect that energy constructively, while agility training and obedience classes provide structure.
Daily dog exercise combats boredom, and positive reinforcement during behavior modification strengthens impulse control, turning destructive habits into healthy enrichment.
When to Seek Veterinary Help for Leg Biting
You need to know when a simple itch crosses the line into something more serious. Certain signs tell you it’s time to call your veterinarian, while you’ve tried home remedies and management strategies. Let’s break down the specific red flags that require professional attention.
Signs of Infection or Complications
When wounds don’t heal properly, infection becomes a real concern. Watch for wound discharge—visible pus or drainage signals bacterial infection in over half of dog bite cases. Redness, swelling, and warmth develop in more than 85% of infected wounds within 48 hours.
Systemic symptoms like fever, lethargy, or swollen lymph nodes mean the infection is spreading and requires immediate veterinarian attention.
Delayed healing, tissue damage, and mobility issues indicate serious complications affecting your dog’s health and wellness.
Monitoring Chronic or Worsening Symptoms
Tracking your dog’s behavior over time reveals patterns that separate a passing irritation from a problem that’s digging in its heels. When paw biting intensifies despite treatment, or new behavioral changes like restlessness emerge, symptom progression demands veterinary follow-up.
Secondary infections can develop quickly, especially with allergies or stress and anxiety underlying the original issue. Your veterinarian will assess treatment efficacy and adjust management strategies accordingly.
Assessing Urgency and Emergency Situations
Certain symptoms cross the line from "call your vet Monday" to "get help now," and recognizing that threshold can prevent minor irritation from escalating into limb-threatening complications. When your dog exhibits these signs, immediate veterinary attention is warranted:
- Severe bleeding that doesn’t stop with direct pressure after several minutes
- Limb swelling accompanied by heat, indicating possible infection or vascular compromise
- Sudden lameness where your dog won’t bear weight on the affected leg
- Breathing difficulty alongside leg biting, suggesting allergic reaction or systemic distress
- Trauma signs like exposed tissue, bone visibility, or wounds penetrating deep muscle layers
These emergency indicators require prompt veterinary intervention to preserve limb function and overall dog health and wellness.
Long-Term Management and Prevention Strategies
Once the crisis passes, your dog needs a sustainable game plan that tackles root causes, not just surface symptoms. Routine Care, Environmental Enrichment, and Consistent Training form your foundation for preventing recurrence of paw biting.
| Strategy | Action Steps |
|---|---|
| Routine Care | Schedule regular checkups every 6-12 months to monitor skin health and catch early warning signs |
| Environmental Enrichment | Provide puzzle toys, varied walking routes, and social interaction to reduce boredom-related paw biting |
| Behavioral Modification | Work with a certified dog trainer to address stress and anxiety in dogs through positive reinforcement |
| Parasite Prevention | Maintain year-round flea, tick, and heartworm control to eliminate common causes of dog paw biting |
| Diet Optimization | Consider hypoallergenic foods or omega-3 supplements if allergies trigger leg biting behaviors |
This proactive approach transforms dog training from reactive crisis management into preventive wellness, giving your dog the best chance at a comfortable, itch-free life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I stop my dog from biting his legs?
Nip it in the bud by first scheduling a veterinary exam to rule out medical causes requiring professional help.
Your vet will assess for infections, allergies, or pain needing wound care or behavioral modification, then recommend preventative measures specific to your dog’s needs.
Is it normal for dogs to bite legs when playing?
Playful leg-biting between dogs is normal dog behavior, reflecting excitement levels and breed tendencies. You’ll notice bite inhibition during play—gentle mouthing without aggression.
Monitor for attention-seeking behavior or excessive intensity, which may require training solutions to prevent escalation.
How do you treat a dog chewing hair off hind legs?
Veterinary care treats the underlying conditions causing hair loss through diagnostic testing and targeted topical treatments.
Your vet will examine your dog for allergies, skin infections, or itchy paws, then recommend behavioral modification alongside preventative measures to stop paw biting and restore healthy fur.
What does it mean when dogs bite their legs?
Picture a dog gnawing relentlessly at the same hind leg spot—this targeted biting signals underlying causes ranging from allergies and paw biting triggers to behavioral indicators of anxiety.
Medical significance increases when scratching persists, as breed predisposition and dog allergy triggers demand owner awareness to prevent complications.
How to stop a dog from biting legs?
Stopping leg biting requires behavioral modification through redirecting behavior with dog training tips, environmental enrichment like puzzle toys, preventative measures including proper wound care, and sometimes professional training to address paw biting triggers effectively.
Are dogs playing when they bite legs?
Some bite patterns during play actually mask discomfort—watch closely. Dogs engaging in puppy play often exhibit playful biting with controlled bite inhibition, showing relaxed body language and reciprocal social signals.
However, attention-seeking behavior or high excitement levels can escalate normal play behavior into problematic paw biting, requiring careful observation of your dog’s overall dog behavior.
How do you know if a dog bite is serious?
A dog bite is serious if you notice deep puncture wounds, uncontrolled bleeding, signs of infection like warmth or pus, suspected nerve damage from numbness, or potential rabies risk.
Your veterinarian should evaluate any bite involving a dog with allergies or underlying disease that punctures skin deeply.
Can certain dog breeds be prone to leg biting?
Genetic factors and breed predispositions can influence leg-biting behavior in canines. Herding breeds may redirect their natural drive, while terrier breeds with hunting instincts might display similar patterns.
Conformation issues in certain dog breeds can contribute to discomfort, triggering abnormal animal behavior.
Does weather impact dogs biting their legs?
Yes, weather directly impacts leg biting in dogs. Winter dryness strips moisture from skin, causing intense itching. Seasonal allergies peak during spring and fall, triggering paw chewing.
Humidity affects flea and tick activity, increasing parasite-related discomfort. Temperature extremes and barometric pressure shifts can worsen inflammation, prompting your dog to bite affected areas for relief.
How does age affect leg-biting behavior?
As the saying goes, you can’t teach an old dog new tricks, but age certainly changes how your dog interacts with their body. Puppy teething drives young puppies to chew and bite at their paws for relief, while senior arthritis and decreased mobility make older dogs focus on painful joints.
Cognitive decline and age-related allergies further complicate the picture as your dog ages.
Conclusion
Like a persistent puzzle that won’t solve itself, the moment your dog starts biting their legs demands more than guesswork. By recognizing whether allergies, infections, pain, or anxiety drives the behavior, you shift from reactive frustration to targeted intervention.
Regular monitoring, veterinary guidance, and environmental adjustments transform chronic irritation into manageable relief. When dogs bite legs, swift action prevents minor discomfort from escalating into serious complications, protecting both skin integrity and long-term well-being.
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6431755/
- https://www.malmlegal.com/personal-injury/illinois-dog-bite-injuries/dog-bite-and-animal-attack-statistics-and-our-recent-dog-bite-ca/
- https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/73087/cdc_73087_DS1.pdf
- https://vcahospitals.com/know-your-pet/bite-wounds-in-dogs
- https://sorensonlaw.net/2023/08/10/dog-bite-risk/