This site is supported by our readers. We may earn a commission, at no cost to you, if you purchase through links.

This condition primarily affects medium to large breeds like Labradors, German Shepherds, and Golden Retrievers between 5-18 months old.
You’ll notice early signs like subtle limping, morning stiffness, or reluctance to play and climb stairs, which are subtle warning signs that most owners miss, and while genetics play the biggest role, rapid growth, overfeeding, and excessive exercise on hard surfaces can worsen the condition.
Treatment ranges from weight management and physical therapy for mild cases to surgical intervention for severe joint damage, and the key lies in recognizing those first subtle warning signs.
Table Of Contents
- Key Takeaways
- What is Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs?
- What Causes Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs?
- Breeds at Higher Risk for Elbow Dysplasia
- Recognizing Symptoms of Elbow Dysplasia
- Diagnosing Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs
- Treatment Options for Elbow Dysplasia
- Preventing and Managing Elbow Dysplasia
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What breeds of dogs have elbow dysplasia?
- How do you treat elbow dysplasia in dogs?
- When can a dog get Elbow dysplasia?
- Is it okay to walk a dog with elbow dysplasia?
- What happens if you don’t treat elbow dysplasia in dogs?
- Can elbow dysplasia in dogs be inherited?
- Are there any breed-specific risk factors for elbow dysplasia?
- Can elbow dysplasia in dogs lead to other joint problems?
- What is the average age of onset for elbow dysplasia in dogs?
- Can elbow dysplasia be completely cured?
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Watch for subtle early signs – You’ll notice limping after exercise, morning stiffness, or reluctance to climb stairs between 5-18 months old, especially in large breeds like Labs and German Shepherds.
- Act fast with proper diagnosis – Don’t wait for obvious symptoms since early X-rays and vet exams can catch the condition before permanent joint damage occurs.
- Manage weight and exercise carefully – You’ll need to keep your dog at an ideal weight and switch to low-impact activities like swimming instead of high-impact running or jumping.
- Consider both surgical and non-surgical options – You can choose from arthroscopic surgery for severe cases or conservative treatment with pain management, supplements, and physical therapy for milder conditions.
What is Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs?
Elbow dysplasia affects the normal development of your dog’s elbow joint, causing cartilage defects and bone growth problems that lead to pain and lameness.
This genetic condition primarily strikes medium-to-large breed puppies between 5 and 18 months old, making it the leading cause of front leg lameness in dogs.
Definition and Overview
When your dog’s elbow joint doesn’t develop properly, it’s called elbow dysplasia.
This genetic predisposition creates cartilage defects and growth abnormalities that cause joint instability.
Canine elbow dysplasia affects the complex elbow joint where three bones meet, leading to elbow malformation.
Dogs with this condition experience pain and mobility issues as abnormal development creates lasting problems in their front legs.
How The Elbow Joint Develops
During the first year, your puppy’s elbow joint undergoes complex development involving three separate bones that must fuse perfectly.
Growth plates regulate bone growth while cartilage formation creates smooth joint surfaces.
Proper nutrient supply supports this intricate process, ensuring joint congruity.
When puppy growth proceeds normally, the elbow joint develops stable connections between bones, maintaining healthy puppy joint health throughout canine developmental disorders prevention, which relies on the proper development of the elbow joint for healthy puppy joint health.
Why It Matters for Dog Health
Beyond affecting your dog’s comfort, elbow dysplasia dogs face serious long-term consequences.
This canine elbow dysplasia creates a domino effect throughout their body, impacting mobility and requiring lifelong pain management. Early elbow dysplasia symptoms signal declining joint health,
while delayed elbow dysplasia treatment compromises quality of life, and protecting canine joint health becomes essential for maintaining lifelong wellbeing and mobility impact.
What Causes Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs?
Elbow dysplasia develops through a combination of genetic inheritance, abnormal bone and cartilage development, and environmental factors that affect your puppy’s growing joints.
While genetics play the primary role, factors like rapid growth, improper nutrition, and excessive exercise during development can worsen the condition.
Genetic Factors and Heredity
Genetics weave a complex tapestry in elbow dysplasia development.
Genetic inheritance threads through every elbow joint, weaving predisposition into your dog’s DNA blueprint
This hereditary condition shows polygenic inheritance patterns, with heritability estimates ranging from 0.16 to 0.34 across canine genetics studies.
Multiple genetic traits contribute to the condition, making gene identification challenging.
While researchers haven’t pinpointed specific mutations, breeding strategies increasingly focus on screening programs to reduce these hereditary conditions in susceptible bloodlines.
Developmental Abnormalities
During elbow development, several abnormalities can disrupt normal joint formation in puppies.
Cartilage defects prevent smooth bone surfaces from developing properly, while uneven bone growth creates joint misalignment.
These developmental issues place excessive joint stress on growing elbows, particularly in large breeds, and hormonal factors also influence how bones mature, potentially worsening elbow dysplasia in genetically predisposed dogs, due to genetic predisposition.
Environmental and Lifestyle Risks
While genetics set the stage, your puppy’s environment plays a major role too.
Poor maternal environment during pregnancy can influence joint development. Excessive puppy exercise on hard surfaces puts extra stress on growing joints, increasing trauma risk.
Diet impact matters – overfeeding leads to rapid weight gain and joint stress. Weight management becomes critical since heavier puppies face higher elbow dysplasia causes through increased mechanical pressure on developing bones.
Proper dog health care is essential to prevent such issues and guarantee overall well-being.
Breeds at Higher Risk for Elbow Dysplasia
While any dog can develop elbow dysplasia, certain breeds face markedly higher risks due to their genetics and rapid growth patterns.
Large and giant breeds are particularly susceptible, with some experiencing rates as high as 40% in affected populations.
Large and Giant Breed Susceptibility
Large and giant dog breeds face higher risks due to their rapid growth rate and skeletal development patterns.
Their genetic predisposition creates unique challenges that breed standards often overlook, making preventative measures and early detection critical for these vulnerable dogs.
Why large breeds struggle more:
- Faster bone growth creates developmental imbalances in elbow joints
- Heavier body weight puts increased stress on developing cartilage
- Hereditary factors concentrate in specific largebreed dogs through selective breeding
- Growth plates close later, extending the vulnerable development period
- Genetics influence how quickly puppies reach adult size and weight
Some breeds, like the Great Pyrenees, are known for their gentle nature. Large and giant dog breeds require special attention due to their unique challenges and genetic predisposition, which can lead to developmental imbalances.
List of Commonly Affected Breeds
Commonly affected breeds include Labrador Retriever, Golden Retriever, German Shepherd, Rottweiler, and Bernese Mountain Dog.
These breeds show significant breed predisposition through genetic screening studies.
Labradors account for 15% of annual cases, while Bernese Mountain Dogs reach 18% prevalence.
Responsible breeding practices and genetic screening help identify at-risk bloodlines.
Puppy selection should prioritize health-tested parents meeting breed standards for elbow health.
Role of Gender and Growth Rate
Gender plays a subtle but measurable role in elbow dysplasia risk, with males showing slightly higher incidence rates than females in large breeds.
Growth rates during puppyhood nutrition periods markedly impact skeletal maturity and growth plates development.
Rapid growth in genetic disease-prone canine genetics can stress developing joints, while hormonal impact during key developmental windows affects bone formation, making controlled growth essential for elbow dysplasia prevention, particularly in relation to elbow dysplasia.
Recognizing Symptoms of Elbow Dysplasia
Recognizing elbow dysplasia symptoms early can help you get your dog the treatment they need before the condition worsens.
You’ll typically notice the first signs in puppies between 5 and 18 months old, though some dogs don’t show obvious symptoms until they’re older.
Early Warning Signs in Puppies
Vigilance becomes your greatest ally when spotting elbow dysplasia in young dogs.
These hereditary conditions often emerge between five and eighteen months, making early detection essential for your puppy’s long-term comfort and mobility.
Watch for these early warning signs:
- Subtle lameness that worsens after exercise or play sessions
- Puppy stiffness in the front legs, especially after rest periods
- Joint swelling around the elbow area that feels warm or puffy
- Gait abnormalities like inward-turning paws or shortened strides
- Reluctance to play or participate in activities they once enjoyed
Progressive Symptoms and Severity
As elbow dysplasia progresses, you’ll notice worsening symptoms that substantially impact your dog’s quality of life.
Early Lameness becomes more pronounced, with limping occurring even without exercise. Joint Degeneration accelerates, causing visible swelling and stiffness. Pain Progression intensifies, making your dog reluctant to move or play. Mobility Decline becomes apparent as arthritis develops, restricting normal activities.
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as optimal nutrition is important for managing joint stress.
Veterinarians use Severity Grading systems to classify the condition’s advancement.
| Mild Progression | Severe Progression |
|---|---|
| Occasional limping after exercise | Constant limping, even at rest |
| Slight joint stiffness in mornings | Severe mobility restrictions daily |
| Mild discomfort during palpation | Visible pain when touching elbow |
| Normal play with brief hesitation | Reluctance to run or jump |
| Subtle gait changes | Obvious abnormal walking patterns |
Chronic and Subtle Clinical Signs
Some dogs mask their pain like stoic warriors, making elbow dysplasia symptoms harder to spot.
Dogs often hide joint pain until it becomes severe, masking early warning signs
You might notice subtle gait changes or mild exercise reluctance that develops gradually.
Joint stiffness after rest periods becomes more apparent, especially during cooler weather.
Your dog may show limping progression that’s inconsistent – present one day, absent the next.
Joint crepitus during movement and persistent arthritis signs warrant professional elbow dysplasia diagnosis.
Diagnosing Elbow Dysplasia in Dogs
Getting an accurate diagnosis requires a thorough veterinary examination that combines physical assessment with specialized imaging techniques.
Your vet will evaluate your dog’s gait, manipulate the elbow joints to check for pain and range of motion.
Then use X-rays or advanced imaging to confirm the diagnosis and determine treatment options.
Clinical Examination and Gait Assessment
Veterinary professionals use several key diagnostic approaches during elbow dysplasia diagnosis.
Lameness grading helps assess severity while your vet watches your dog walk and trot.
Palpation techniques reveal joint pain, stiffness, and swelling through careful touch.
Range of motion testing identifies movement limitations.
Joint crepitus, that grinding sound, indicates cartilage damage.
Posture analysis examines how your dog stands and moves, revealing compensatory behaviors that signal underlying problems.
It also involves assessing how your dog moves.
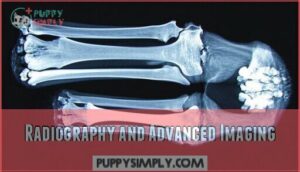
Radiography and Advanced Imaging
After your vet’s clinical exam, radiographs become the cornerstone of diagnosis. Your veterinary radiologist will analyze these X-rays using specific radiographic positioning techniques to reveal bone abnormalities and joint incongruity.
- Standard radiographs detect 88.8% of elbow dysplasia cases through careful image interpretation
- CT scans provide three-dimensional views when X-rays appear normal but symptoms persist
- MRI findings offer superior soft tissue contrast for cartilage assessment in complex cases
Advanced veterinary diagnostics through canine radiology help catch subtle changes before arthritis develops. Early diagnosis is essential to prevent the development of osteoarthritis in dogs.
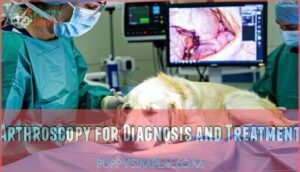
Arthroscopy for Diagnosis and Treatment
When X-rays can’t reveal the full picture, arthroscopy becomes your veterinarian’s detective tool.
This minimally invasive procedure uses a tiny camera to examine joint cartilage directly, providing both diagnosis and treatment in one session.
| Arthroscopic Techniques | Benefits | Recovery Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Fragment removal | Direct visualization | 6-8 weeks restricted activity |
| Cartilage assessment | Smaller incisions | 2-3 days hospitalization |
| Joint debridement | Faster healing | 12-16 weeks full recovery |
Post-op care involves controlled exercise and pain management for ideal elbow dysplasia surgery outcomes.
Treatment Options for Elbow Dysplasia
When your dog receives an elbow dysplasia diagnosis, you’ll need to choose between surgical and non-surgical treatment approaches based on the severity of the condition.
The right treatment plan depends on your dog’s age, the extent of joint damage, and how much the condition affects their daily activities.
Non-Surgical Management Strategies
Managing elbow dysplasia without surgery requires a thorough approach that focuses on comfort and mobility.
Conservative treatment can effectively slow disease progression and maintain your dog’s quality of life through targeted interventions.
- Weight Control – Maintain ideal body condition to reduce joint stress and inflammation
- Exercise Modification – Replace high-impact activities with controlled, low-impact movement like swimming
- Joint Supplements – Provide glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids for cartilage support
- Pain Management – Use NSAIDs and anti-inflammatory medications as prescribed by your veterinarian
- Physical Therapy – Incorporate range-of-motion exercises and physiotherapy to maintain joint function
Numerous options exist for dog joint care.
Surgical Treatment Options
When conservative treatment fails, surgical intervention becomes necessary for your dog’s elbow dysplasia.
Arthroscopic surgery offers the least invasive approach for fragment removal and joint realignment. Ulnar osteotomy corrects bone alignment issues, while severe cases may require joint replacement.
Each elbow dysplasia surgery targets specific abnormalities to restore function and reduce pain. Post-surgery, pet owners often seek supportive care products for their dogs.
Recovery, Rehabilitation, and Prognosis
Recovery from elbow dysplasia surgery requires patience, as your dog’s journey back to normal activity takes time.
Post-op care includes 2-4 weeks of strict cage rest, followed by gradual activity increases over 8 weeks.
Physical therapy and canine rehabilitation, including hydrotherapy sessions, substantially improve elbow dysplasia recovery outcomes.
Pain management through NSAIDs helps comfort during healing.
Joint supplements support long-term joint health.
The elbow dysplasia prognosis varies – while 60-90% of dogs regain satisfactory function, chronic arthritis often develops, requiring ongoing management for the best canine joint disease prognosis.
Preventing and Managing Elbow Dysplasia
While you can’t completely prevent elbow dysplasia in genetically predisposed dogs, you can take steps to reduce risk and manage the condition effectively.
Responsible breeding practices, proper nutrition during growth, and early intervention can make a significant difference in your dog’s quality of life.
Responsible Breeding and Screening
Smart breeding prevents more elbow dysplasia than any treatment.
Reputable breeders use genetic testing and hip scoring to screen parents for canine hereditary conditions.
Here’s what ethical breeding involves:
- OFA elbow certification for both parents before mating
- DNA testing for elbow dysplasia genetics markers
- Breeder transparency about health records and lineage
- Puppy selection guidance based on family history
- Written health guarantees covering joint development
Choose dog breeding programs that openly share screening results and pedigree health data.
Weight and Exercise Management
Weight control and controlled exercise form the backbone of managing elbow dysplasia. You’ll need to monitor your dog’s body condition regularly, as excess weight increases joint stress.
Low-impact activities like swimming offer hydrotherapy benefits without jarring movements. Post-exercise care includes rest and joint supplements to support cartilage health.
Many owners find added comfort using supplements to be beneficial in managing their dog’s condition.
| Exercise Type | Benefits | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Swimming/Hydrotherapy | Low-impact joint movement | 2-3 times weekly |
| Leash walks | Controlled pace and distance | Daily, 20-30 minutes |
| Physical therapy | Targeted muscle strengthening | As prescribed |
| Free play | Natural movement patterns | Limited sessions |
| High-impact activities | Should be avoided | Never recommended |
It’s essential to follow a routine that includes controlled exercise and rest to ensure the dog’s joints are not overstrained, promoting overall health and well-being.
Supportive Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
Beyond proper weight control, thorough elbow dysplasia management requires thoughtful home modifications and assistive devices.
These supportive measures enhance your dog’s comfort while addressing pain management and mental wellbeing needs.
Strategic environmental changes support elbow dysplasia physiotherapy goals and maintain social interaction opportunities.
- Install non-slip rugs and ramps to reduce joint stress during daily movement
- Provide orthopedic bedding and raised food bowls for comfortable positioning
- Use harnesses instead of collars to avoid pulling pressure on front limbs
- Create low-impact exercise routines combining swimming with gentle elbow dysplasia exercises
- Establish consistent pain management protocols including supplements and prescribed medications
Maintaining optimal canine health is also vital for managing elbow dysplasia and improving overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What breeds of dogs have elbow dysplasia?
Over 160 breeds face elbow dysplasia risk, with rates reaching 50% in some lines. You’ll find it most commonly affects large breeds like Labrador Retrievers, German Shepherds, Golden Retrievers, and Rottweilers.
How do you treat elbow dysplasia in dogs?
You’ll need to work with your vet to create a treatment plan that combines surgery and medical management.
Surgical options include arthroscopic procedures to remove bone fragments or realign joints.
Medical management involves weight control, anti-inflammatory medications, joint supplements, and controlled exercise to manage pain.
When can a dog get Elbow dysplasia?
Unfortunately, your furry friend can develop elbow dysplasia surprisingly early – typically between 5-18 months old during their rapid growth phase, though some signs don’t appear until age 3-
Is it okay to walk a dog with elbow dysplasia?
Yes, you can walk your dog with elbow dysplasia, but keep walks short, on soft surfaces, and avoid hills or stairs.
Gentle, controlled exercise helps maintain joint mobility without worsening pain or inflammation, which is a complete concept for managing elbow dysplasia in dogs.
What happens if you don’t treat elbow dysplasia in dogs?
While many think it’s just limping, untreated elbow dysplasia causes chronic pain, severe arthritis, and permanent joint damage.
Your dog’s mobility will progressively worsen, potentially leading to complete lameness and substantially reduced quality of life, due to severe arthritis.
Can elbow dysplasia in dogs be inherited?
Elbow dysplasia has a strong genetic component, with heritability estimates ranging from 16 to
If you’re breeding dogs, you’ll want to screen parents since affected dogs can pass this condition to their puppies through inherited traits.
Are there any breed-specific risk factors for elbow dysplasia?
Breed-specific factors play a huge role in your dog’s risk.
Large breeds like German Shepherds, Golden Retrievers, and Labradors face dramatically higher rates—some reaching 40-50% incidence compared to minimal risk in smaller breeds.
Can elbow dysplasia in dogs lead to other joint problems?
Unfortunately, this condition doesn’t stay put – it’s like opening Pandora’s box.
You’ll find that elbow dysplasia often triggers compensatory problems in your dog’s shoulders, spine, and opposite limbs as they shift weight to avoid pain.
What is the average age of onset for elbow dysplasia in dogs?
You’ll typically notice signs developing between 5 and 18 months of age, with most symptoms appearing before your dog reaches 3 to 4 years old.
Can elbow dysplasia be completely cured?
No, elbow dysplasia can’t be completely cured. You can manage symptoms through surgery, medication, and lifestyle changes, but arthritis will likely develop over time, requiring lifelong treatment.
Conclusion
Managing elbow dysplasia in dogs demands dedication, diligence, and decisive action from responsible pet owners.
You’ve learned that early detection makes the difference between manageable discomfort and debilitating arthritis.
Whether you’re choosing a puppy from health-tested parents or managing an affected dog through weight control and appropriate exercise, your proactive approach directly impacts your dog’s quality of life.
Remember that elbow dysplasia in dogs doesn’t have to mean a life of pain when you combine veterinary expertise with consistent, thoughtful care.
- https://pets.webmd.com/dogs/dogs-arthritis-directory
- http://image.petmd.com/files/2025-03/Elbow%20dysplasia%20in%20dog.pdf?VersionId=U2hBwHhx3oLh7RWNXgYQCwOcv8BsE5N_
- https://www.acvs.org/small-animal/canine-elbow-dysplasia/
- https://pangovet.com/?utm_source=dogster&utm_medium=article&utm_campaign=dogster_general
- https://ofa.org/diseases/disease-statistics/